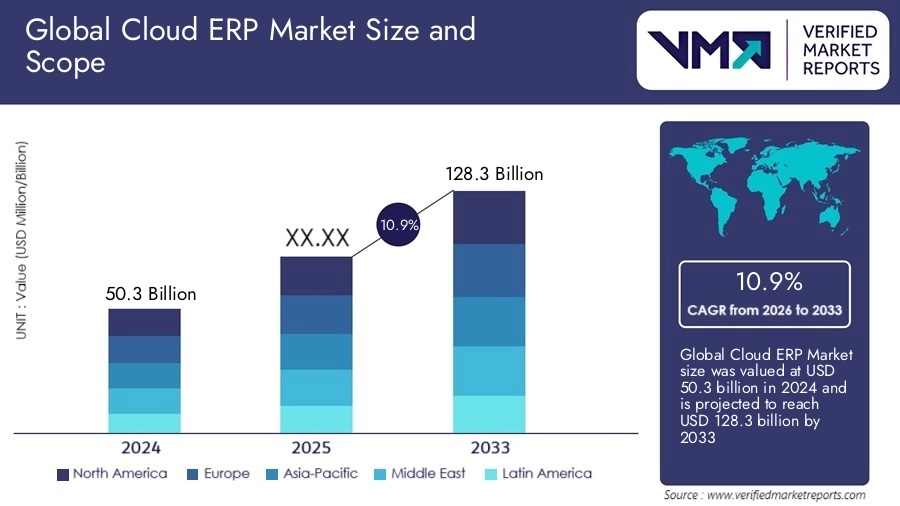
The global cloud ERP market is poised for substantial expansion, with Verified Market Reports projecting growth from $50.3 billion in 2024 to $128.3 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 10.9%. The surge reflects enterprises’ intensifying focus on scalability, real-time data access, and operational efficiency as cloud-based platforms become the dominant deployment model for mission-critical business systems.
Market Dynamics Reshape Enterprise Operations
For technology executives navigating digital transformation initiatives, cloud ERP adoption delivers measurable productivity gains that fundamentally alter operational workflows. Organizations implementing cloud ERP report 66% improvement in operational efficiency driven by automated workflows and real-time data access, with 78% productivity gains and 91% inventory optimization. Manufacturing companies using cloud-based ERP systems have reduced inventory levels by 38% while increasing production efficiency by 18% within the first year of deployment.
The financial impact proves equally compelling, with average ROI reaching 52%, meaning every dollar invested returns $1.52 in value, and payback periods averaging 2.5 years. Omega Industries demonstrated cloud ERP’s resilience during a cyberattack that caused a three-week outage, with their cloud-based system ensuring uninterrupted billing and vendor payments when on-premise infrastructure failed. Current data shows 70.4% of ERP deployments now operate in the cloud as of 2024, up from 69.8% the previous year, signaling steady migration from legacy systems.
However, transformation challenges persist beyond technology implementation. Data migration remains one of the most underestimated risks, with inconsistent master data, inaccurate records, and legacy data structures multiplying complexity during cutover. Organizations must prioritize comprehensive testing as underestimating this phase creates poor quality post-go-live experiences.
Technology executives evaluating cloud ERP providers should prioritize real-time access across multiple locations, industry-specific capabilities, and clean core principles that minimize custom code while leveraging modular extensions. The clean core approach ensures upgradability and flexibility as vendors deliver continuous innovation. Integration of AI-driven technologies enables automation of tedious tasks and improved supply chain operations, while proliferation of IoT devices creates more sophisticated data management capabilities within ERP systems.
What This Means for ERP Insiders
Clean core architecture becomes competitive differentiator. SAP’s emphasis on clean core principles and modular extensions signals fundamental shift in vendor product strategy away from customization tolerance toward standardized best practices. GSIs and transformation leaders must reposition consulting practices from custom development to process standardization, while enterprise architects should prioritize API-driven integrations over legacy modifications to maintain platform upgradability and access continuous innovation cycles.
Cloud deployment economics force recalibration of on-premise business cases. With 70.4% of ERP deployments already cloud-based and average ROI of 52% within 2.5 years, on-premise total cost of ownership arguments weaken substantially. ERP vendors maintaining hybrid strategies face margin pressure as development resources split between cloud innovation and legacy maintenance, while SIs should accelerate cloud competency development as the remaining 30% on-premise installations represent shrinking revenue pools concentrated in specialized regulatory environments or mid-migration transitional states.
Data migration emerges as primary transformation risk. Data quality, cleansing, and migration as most underestimated risks, with inconsistent master data creating post-go-live operational issues. This pattern indicates opportunity for specialized data migration tooling, services, and governance frameworks, while also signaling that transformation leaders must shift project resource allocation toward data workstreams earlier in implementation lifecycles to prevent schedule overruns that studies show plague compressed migration timelines.